Exploring 4D Radar ANPR Cameras’ Multi-Dimensional Capabilities
In the sector of surveillance and security, technological advancements continually push boundaries, enabling solutions that were once considered modern. Among these innovations, Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) systems have emerged as a foundation in modern-day monitoring and enforcement strategies. Traditional ANPR cameras rely mostly on visual data, capturing license plate information through optical means. However, the evolution of technology has ushered in a new era with the arrival of 4D Radar ANPR cameras, exceeding the limitations of visuals and introducing multi-dimensional capabilities. In this comprehensive exploration, we look into the complexity of 4D Radar ANPR cameras, Understanding their significance and potential in revolutionizing surveillance landscapes.
Table of Contents
Understanding 4D Radar ANPR Cameras:
At the heart of 4D Radar ANPR cameras considering a complex combination of radar technology and ANPR systems. Unlike their conventional counterparts, which primarily rely on optical sensors, 4D Radar ANPR cameras integrate radar modules, enabling them to observe dimensions beyond simple visuals. This integration empowers these cameras with the ability to capture, analyze, and interpret data in real time, transcending traditional constraints associated with lighting conditions, weather variations, and visual obstructions.

The term “4D” encapsulates the four-dimensional nature of these cameras, which includes physical dimensions along with the temporal aspect. While conventional ANPR cameras operate in three physical dimensions, 4D Radar ANPR cameras introduce the fourth dimension of time, enabling them to track and analyze dynamic movements with unparalleled accuracy. This temporal dimension equips these cameras with predictive capabilities, facilitating the anticipation of vehicle directions and behaviors, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and situational awareness.
Key Components and Working Mechanism:
To comprehend the functionality of 4D Radar ANPR cameras, it’s imperative to break apart their key components and working mechanisms. At the core of these cameras incorrect information from a radar sensor array, including transmitters and receivers that emit electromagnetic waves and capture their reflections from surrounding objects. Unlike optical sensors, radar modules are immune to environmental factors such as darkness, clouds, and harmful weather conditions, ensuring consistent performance in different scenarios.
Upon detecting a vehicle within its field of view, the radar module generates a raw data stream containing information about the vehicle’s position, velocity, and orientation. This data stream is then processed by advanced algorithms, which extract relevant features such as license plate details and vehicle characteristics. Making Use of machine learning and pattern recognition techniques, the camera identifies and verifies license plate information with high accuracy, even in challenging scenarios characterized by high speeds or difficulties.
The combination of radar and ANPR technologies enables 4D Radar ANPR cameras to overcome traditional limitations associated with optical sensors. By augmenting visual data with spatial and temporal information, these cameras offer enhanced capabilities in scenarios where traditional ANPR systems fall short, such as low-light conditions, high-speed environments, or congested traffic.

Applications and Use Cases:
The flexibility of 4D Radar ANPR cameras exceeds conventional surveillance applications, finding utilization across different domains from law enforcement to smart city initiatives. Some important applications include:
Traffic Management and Law Enforcement:
- 4D radar ANPR cameras play an important role in traffic management and law enforcement by accurately capturing license plate information.
- They enable authorities to monitor traffic flow, enforce speed limits, detect stolen vehicles, and identify vehicles involved in illegal activities.
- Integration with backend systems allows for real-time alerts and automated ticketing, streamlining law enforcement operations.
Parking Management:
- In parking facilities, 4D radar ANPR cameras streamline entry and exit processes by automatically identifying vehicles and managing access control.
- They provide efficient parking space utilization by tracking occupancy in real-time, reducing congestion, and improving overall customer experience.
- Integration with payment systems enables seamless payment processing, eliminating the need for physical tickets or manual assistance.
Border Control and Homeland Security:
- 4D radar ANPR cameras enhance security measures at border checkpoints and high-security areas by accurately identifying vehicles and screening for potential threats.
- They facilitate the tracking of vehicles entering and exiting restricted zones, supporting the enforcement of border control policies and the prevention of illegal entry and smuggling activities.
- Advanced analytics capabilities enable authorities to analyze vehicle movement patterns and identify suspicious behavior for proactive involvement.
Toll Collection and Road Pricing:
- 4D radar ANPR cameras are widely deployed in toll collection systems and road pricing schemes, automating the process of charging vehicles based on usage.
- By capturing license plate information without needing toll booths or manual toll collection, they improve traffic flow and reduce congestion on highways and toll roads.
- Integration with backend billing systems ensures accurate billing and seamless revenue collection for transportation authorities.
Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development:
- Municipalities utilize 4D Radar ANPR cameras as integral components of smart city initiatives, enabling data-driven decision-making in urban planning and infrastructure development.
- By analyzing traffic patterns and vehicular movements, these cameras provide insights into transportation dynamics, facilitating the optimization of road networks and public transportation systems.
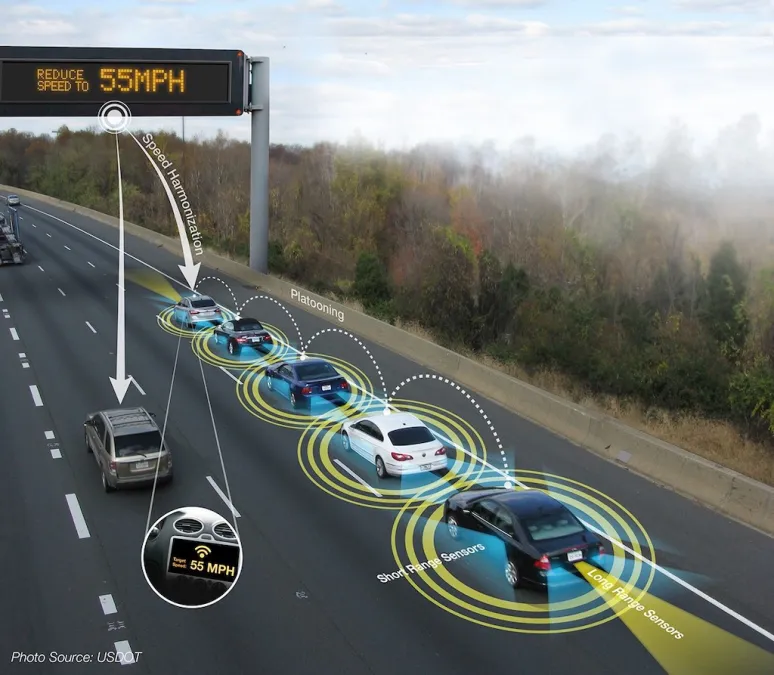
Challenges and Considerations:
While 4D Radar ANPR cameras offer plenty of benefits, their deployment comes with certain challenges and considerations:
Cost and Infrastructure Requirements:
- The integration of radar technology increases the cost of 4D Radar ANPR cameras compared to conventional ANPR systems, necessitating important investment for deployment.
- Additionally, the installation of radar sensors may require additional infrastructure such as Mounting supports or power sources, adding complexity to deployment efforts.
Data Privacy and Security:
- The extensive data captured by 4D Radar ANPR cameras raises concerns regarding privacy infractions and data security.
- To address these concerns, exact protocols, and encryption mechanisms must be implemented to safeguard sensitive information and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Integration and Interoperability:
- Seamless integration with existing surveillance infrastructure and backend systems poses a challenge, particularly in environments characterized by different technologies and exclusive standards.
- Collaboration issues may occur when attempting to interface 4D Radar ANPR cameras with legacy systems, necessitating standardized protocols, and middleware solutions.
Advantages of 4D Radar ANPR Cameras
The adoption of 4D radar ANPR cameras brings forth a myriad of advantages across various domains:
Unparalleled Accuracy:
Unlike optical sensors susceptible to closing and environmental interference, 4D radar ANPR cameras deliver unparalleled accuracy in license plate recognition. Their ability to enter through negative weather conditions ensures reliable operation and minimizes false positives, thereby enhancing overall system performance.
Extended Surveillance Range:
Integrating radar technology, 4D ANPR cameras offer an extended surveillance range compared to conventional optical cameras. This enables monitoring of expansive areas and facilitates early detection of security breaches or suspicious activities, enhancing border protection and threat mitigation measures.
Adaptive Performance:
Equipped with radar imaging capabilities, 4D radar ANPR cameras show adaptive performance under varying environmental conditions. When faced with low visibility, negative weather, or fluctuating lighting conditions, these cameras maintain consistent operation, ensuring uninterrupted surveillance coverage and situational awareness.
Real-Time Monitoring and Analysis:
By capturing dynamic changes within the surveillance environment in real time, 4D radar ANPR cameras empower operators with timely insights and actionable intelligence. This facilitates proactive decision-making, swift response to security incidents, and efficient allocation of resources, thereby enhancing overall operational effectiveness.
Cost-Effectiveness and Return on Investment:
While offering advanced surveillance capabilities, 4D radar ANPR cameras prove cost-effective in the long run. Their durability, reliability, and low maintenance requirements translate into reduced operational costs and enhanced return on investment, making them an attractive investment for organizations looking to optimize their security infrastructure.
Future Directions and Innovations:
The evolution of 4D Radar ANPR cameras continues uninterrupted, motivated by ongoing research and technological advancements. Some promising avenues for future innovation include:

Enhanced Predictive Analytics:
- Making Use of the temporal dimension offered by 4D Radar ANPR cameras, advancements in predictive analytics algorithms hold the potential to forecast vehicle paths and anticipate traffic patterns with greater accuracy.
Edge Computing and Real-Time Decision Making:
- The integration of edge computing capabilities within 4D Radar ANPR cameras enables real-time data processing and decision-making at the network edge, minimizing latency and enhancing responsiveness in critical scenarios.
Multi-Sensor Fusion:
- Integrating additional sensor methods such as LiDAR or thermal imaging with 4D Radar ANPR cameras enriches the contextual awareness of surveillance systems, enabling comprehensive monitoring capabilities across different environmental conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, 4D Radar ANPR cameras represent a structure shift in the field of surveillance and security, transcending the limitations of traditional ANPR systems through the integration of radar technology and multi-dimensional analytics. By enhancing visual data with physical and temporal information, these cameras offer unparalleled capabilities in vehicle detection, tracking, and license plate recognition across different scenarios and environments. While challenges such as cost, privacy, and Integration continue, the ongoing advancements in technology promise to further enhance the effectiveness and versatility of 4D Radar ANPR cameras, creating the way for a safer, smarter, and more secure future.

