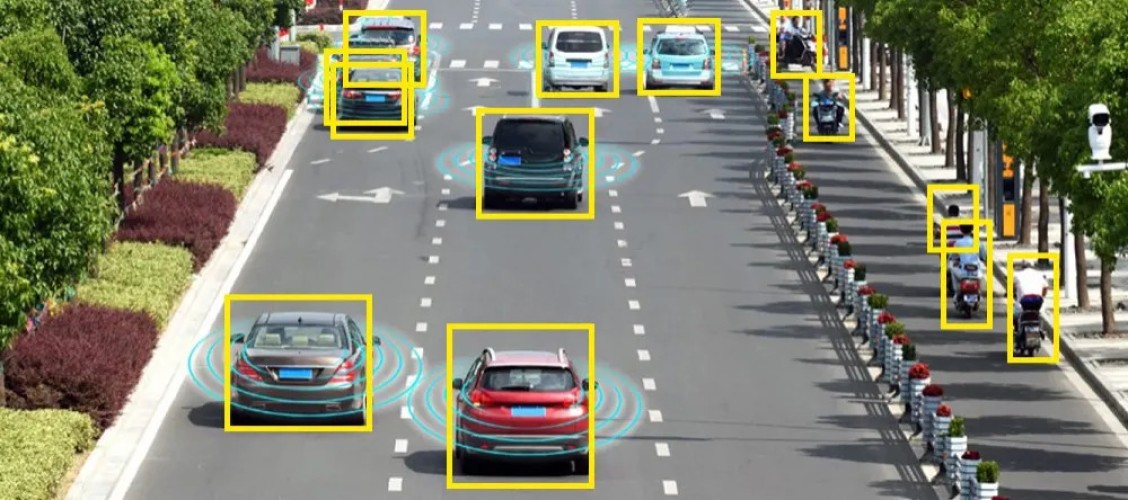
ATCC: Smart Road for a Smoother Future
Since the earth is becoming more urbanized, traffic management is becoming a significant issue for cities worldwide. In addition to wasting time and fuel, traffic jams also contribute to atmospheric pollution and lead to a declining standard of living. Automated surveys and other conventional traffic monitoring methods fall short of addressing the complexity of current traffic movements.
Given that the Automatic Traffic Counter and Classifier (ATCC) have been developed, there is an effective solution that might completely alter how traffic is managed. We are going to get into the exciting area of intelligent roads and examine the complicated nature of ATCC technology in this extensive blog post. Let’s go on an adventure into smart roads, learning how these cutting-edge technologies function, analyzing their effects on traffic control, and imagining a better future.
Table of Contents
ATCC Need for Smart Roads and Intelligent Traffic Management System:
Around the world, cities are experiencing significant development and population growth, which has put great strain on the transport system. Therefore, passengers now have to contend with traffic jams daily. Current traffic control techniques, such as hand-counted inquiries, take a lot of time and money and do not provide the accuracy needed to handle the changing character of the traffic management system. Automatic Traffic Counter and Classifier have the potential to change traffic management, improving the intelligence and effectiveness of our roads.

Such smart highways’ core components are intelligent traffic management systems (ITMS). They collect data from ATCC sensors in various places, examine the data instantly, and produce valuable conclusions. Traffic engineers and municipal authorities can use ITMS to optimize traffic movement, increase general safety on the roads, and develop predictions based on data.
How Does ATCC Work?
The roadway system comes with a network of advanced sensors and technologies known as the Automatic Traffic Counter and Classifier. These sensors can be found in many different configurations, such as radar, magnetic loops, and video analytics. Let’s examine the operation of every one of these technologies:
Radar-Based Counters:
Radio signals are used by radar systems to identify and monitor moving vehicles. The radar system can determine a vehicle’s speed, size, and location once it passes the detecting zone since it bounces radio signals back into the sensor. Radar-based monitors are very useful in bad weather and can deliver exact information through rainfall or clouds.
Inductive Loop Sensors:
Magnetic fields are used by inductive loops to identify the condition of moving objects. The sensors produce a magnetic signal that is inserted across the road’s surface. The field is disturbed when a car drives through the loop, allowing the detector to detect the car’s position and speed. Traffic classification and counting are popular applications for magnetic loop sensors because of their outstanding reliability.
Video Analytics:
Cameras are used through video-based automatic traffic counters to collect real-time traffic statistics. To recognize and track cars, complicated algorithms analyze the video stream to calculate their number, speed, and categorization. Video analytics provide a thorough overview of traffic, which makes them essential in traffic control and strategy.
The Power of Real-Time Data:
One of the key benefits of an automatic traffic counter and classifier is their ability to provide up-to-date information on traffic conditions. Thanks to ATCC technology, officials can now quickly monitor the flow of traffic, which is significantly quicker than previous systems that may take days or possibly weeks to gather data. This recent data makes it easy to analyze traffic advancements, discover problems with traffic, and take early measures to optimize traffic movement.
With the most up-to-date information, ITMS can also change the timing of highway signals to improve traffic movement. By self-adjusting signal moments, preserving smooth traffic flow, and reducing overall overcrowding, smart roads can adapt to changing traffic patterns.

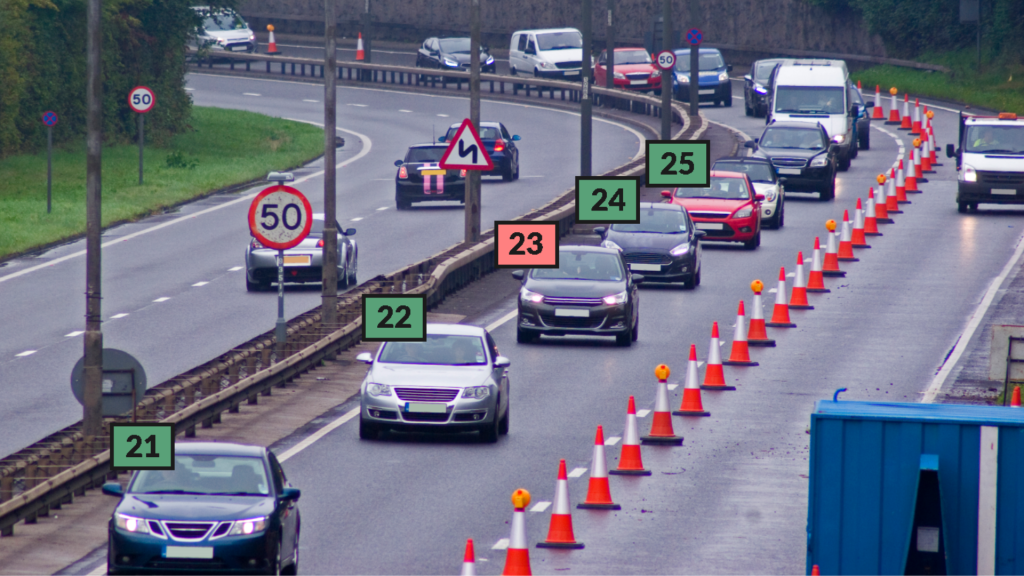
Accurate Vehicle Counting for Enhanced Traffic Analysis:
Automatic traffic counters’ vital role is to offer exact vehicle reporting. Officials can predict traffic numbers at particular places because of these devices’ ability to count vehicles as they pass across their sensors. A correct count of vehicles improves the understanding of heavy traffic periods, the identification of high-traffic regions, and the development of focused congestion-relief strategies by traffic engineers and developers.
Also, governments could more successfully distribute resources if they had accurate information on the flow of traffic. For example, to satisfy growing needs, transportation options may be improved during busy times.
Classifying Vehicles for Deeper Traffic Analysis:
Automatic Traffic Classifiers improve traffic observation above simple tracking of vehicles by categorizing them according to size, kind, and speed. These classifiers differentiate between automobiles, lorries, motorbikes, cycles, and people walking, giving users a thorough insight into the makeup of the flow of traffic.
Vehicle classification data is crucial for effective transportation planning and infrastructure development. For instance, it helps in designing roads that can withstand the weight of heavy trucks, identifying the need for dedicated bicycle lanes, or implementing safety measures tailored to specific vehicle types.
Improving Road Safety and Efficiency:
One of the most significant advantages of smart roads empowered by Automatic Traffic Counters and Classifiers is improved road safety. Real-time data and analysis provided by ATCC technology enable authorities to detect traffic incidents and accidents promptly. Intelligent Traffic Management Systems (ITMS) can immediately alert relevant emergency services, helping reduce response times and potentially saving lives.
Additionally, automatic traffic counters and classifiers play a vital role in implementing adaptive traffic control systems. These systems adjust traffic signal timing based on real-time traffic conditions, ensuring smooth traffic flow and minimizing the chances of bottlenecks.
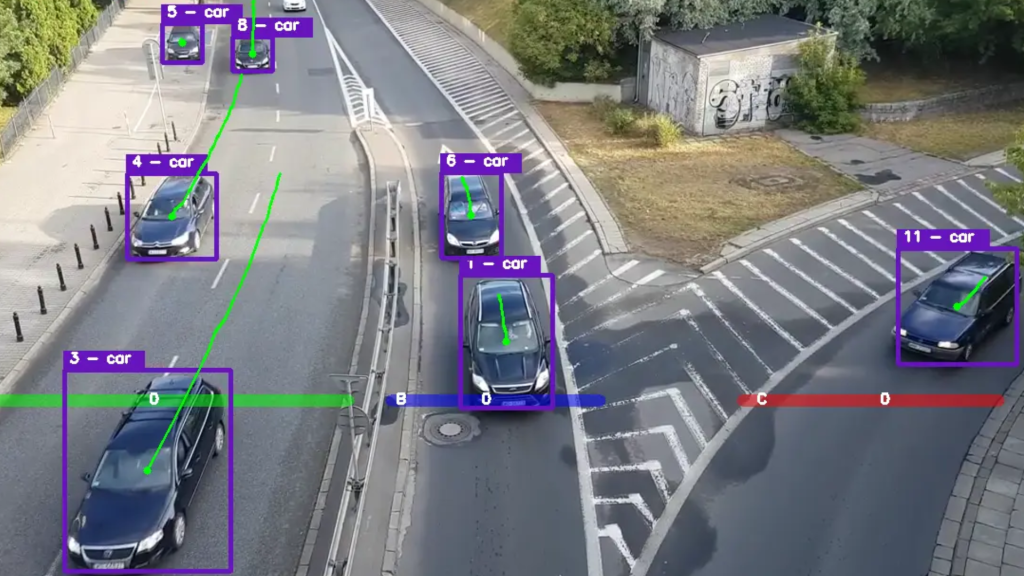
Smart Roads: Enabling Sustainable Urban Mobility
As cities strive for sustainability and greener transportation options, smart roads have become an essential component of sustainable urban mobility strategies. By reducing traffic congestion and optimizing traffic flow, Smart Roads can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. The efficient use of public transport options, facilitated by real-time data from ATCC technology, can encourage more people to use public transit, further reducing the number of vehicles on the road.
Incorporating smart roads into urban planning can also lead to a more pedestrian-friendly environment. Accurate pedestrian counting data enables authorities to design safer crossings and sidewalks, promoting walking as a viable means of transport.
The Role of Data Privacy and Security:
While the potential benefits of smart roads and ATCC technology are immense, data privacy and security are critical concerns that must be addressed. Collecting and analyzing real-time traffic data involves dealing with a vast amount of sensitive information, including vehicle counts, speeds, and classifications. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data is essential to maintaining public trust and confidence in technology.
Authorities and technology providers must adhere to stringent data protection measures, secure data transmission protocols, and anonymization practices to safeguard user privacy. Transparent communication with the public about data usage and data retention policies is vital to creating a responsible and trustworthy Smart Roads ecosystem.
Challenges and Future Directions:
While Automatic Traffic Counters and Classifiers offer exciting possibilities for smarter traffic management, several challenges need to be addressed. These include the cost of deploying and maintaining the technology, integration with existing transportation infrastructure, and the need for standardized data formats across different vendors.

The future of Smart Roads holds tremendous potential. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more sophisticated ATCC devices capable of capturing additional data points, such as vehicle emissions, weather conditions, and road surface conditions. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms could further enhance the capabilities of ATCC technology, allowing for predictive traffic analysis and more efficient traffic management.
Conclusion:
Automatic Traffic Counters and Classifiers have emerged as a game-changing technology that promises to reshape the way we manage traffic in our cities. Through real-time data, precise vehicle counting, and vehicle classification, Smart Roads empowered by ATCC technology can optimize traffic flow, enhance road safety, and promote sustainable urban mobility.
However, the successful implementation of Smart Roads relies on a collaborative effort involving city authorities, technology providers, and the public. Ensuring data privacy and security, addressing infrastructure challenges, and investing in ongoing research and development are crucial steps toward building a future where Smart Roads pave the way for a smoother and more efficient transportation network. With ATCC technology at the helm, we are one step closer to realizing the vision of a smarter, safer, and more sustainable future for our cities and communities.